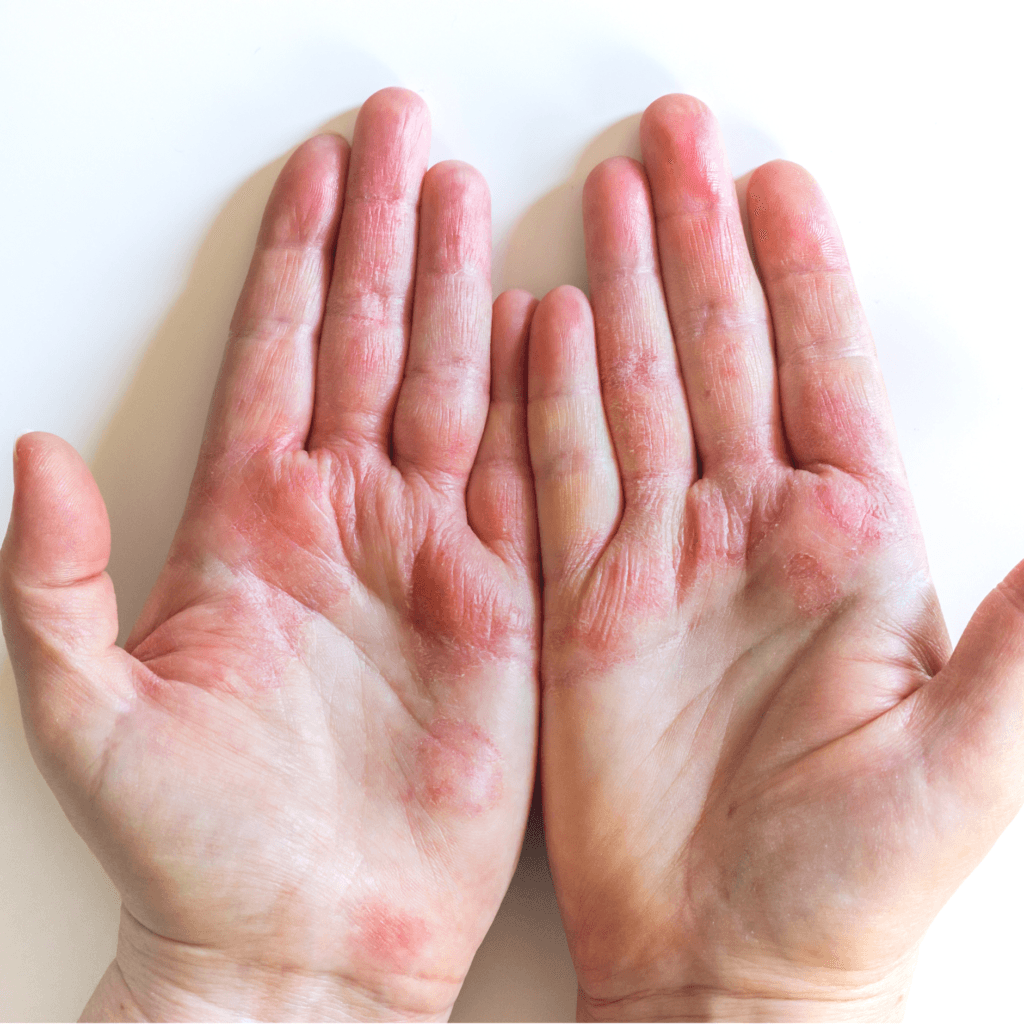
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition affecting millions worldwide. Understanding this condition, characterized by inflamed, itchy, and red patches of skin, is crucial. With the proper knowledge and care, it is possible to reduce the severity of symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected. In this blog post, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies for eczema, empowering you with the information you need.
WHAT IS ECZEMA?
Eczema is a group of conditions that cause the skin to become red, itchy, and inflamed. The most common type is atopic dermatitis, which often starts in childhood and can persist into adulthood. Other types of eczema include:
- Contact dermatitis
- Dyshidrotic eczema
- Seborrheic dermatitis
CAUSES OF ECZEMA
The exact cause of eczema is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to genetic and environmental factors. The common triggers include:
Genetics
A family history of eczema, asthma, or allergies increases the likelihood of developing eczema.
Environmental Triggers
Common irritants such as soaps, detergents, pollen, and dust mites can trigger eczema flare-ups.
Allergens
Exposure to pet dander, certain foods, and environmental allergens can exacerbate symptoms.
Climate
Cold, dry weather can dry out the skin, leading to eczema flare-ups, while hot, humid conditions can cause sweating, which may also trigger symptoms.
Stress
Emotional stress can worsen eczema symptoms, leading to more frequent flare-ups.
SYMPTOMS OF ECZEMA
Eczema symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
Itchy Skin
Intense itching is a hallmark symptom of eczema and can be exceptionally bothersome at night.
Red or Brownish Patches
Inflamed areas of skin that may appear red, brown, or grey
Dry, Scaly Skin
Eczema often causes the skin to become dry, cracked, and scaly.
Blisters
In some cases, small, fluid-filled blisters may develop and ooze.
Thickened Skin
Repeated scratching can cause the skin to thicken and become leathery in texture.
Eczema can affect any part of the body, but it commonly appears on the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, and the inside bend of the elbows and knees.
EFFECTIVE MANAGEMENT STRATEGIES FOR ECZEMA
While eczema has no cure, you play a crucial role in managing it. Several management strategies can help reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Here are some practical approaches that, when implemented by you, can make a significant difference:
MOISTURIZE REGULARLY
Keeping the skin hydrated is one of the most critical steps in managing eczema. Regular moisturizing helps prevent dryness and reduces itching:
Use Emollients
Apply fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizers, creams, or ointments several times daily, especially after bathing.
Ointments over Creams
Ointments tend to be more effective at sealing in moisture compared to creams or lotions, especially in cold or dry climates.
Soak and Seal
After bathing, pat the skin dry and apply a thick layer of moisturizer while the skin is still damp to lock in moisture.
IDENTIFY AND AVOID TRIGGERS
Identifying what triggers your eczema flare-ups can help you manage the condition more effectively:
Patch Testing
Consult a dermatologist for patch testing. This involves applying small amounts of potential allergens to your skin and observing for any reactions. Patch testing can help identify specific allergens or irritants causing your eczema flare-ups, allowing you to avoid them in the future.
Mild Cleansers
Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers and avoid products with harsh chemicals or artificial fragrances.
Wear Soft Fabrics
Choose clothing made from soft, breathable fabrics like cotton and avoid rough materials like wool that can irritate the skin.
MANAGE STRESS
Since stress can trigger eczema, finding ways to manage stress is essential. Stress can weaken the immune system and increase inflammation, which can exacerbate eczema symptoms. Incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation into your daily routine can help reduce stress and manage your eczema.
Relaxation Techniques
Incorporate relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, yoga, or meditation into your daily routine.
Adequate Sleep
Ensure you get enough rest, as sleep is vital for overall skin health and stress management.
MEDICATIONS AND TREATMENTS
In some cases, medications or other treatments may be necessary to manage eczema:
Topical Corticosteroids
These anti-inflammatory creams or ointments can help reduce itching and inflammation during flare-ups.
Oral Medications
Doctors may prescribe oral corticosteroids, antihistamines, or immunosuppressants in more severe cases.
Light Therapy
Also known as phototherapy, this treatment involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial light to reduce inflammation and itching.
STAY HYDRATED AND FOLLOW A HEALTHY DIET
Hydration
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to keep the skin hydrated from the inside out.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
To help reduce inflammation and support skin health, include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins (such as fish, leafy greens, nuts, and seeds).
Avoid Trigger Foods
Some people with eczema may have food sensitivities or allergies. Common triggers include dairy, gluten, and soy. Keeping a food diary can help identify any problematic foods.
Eczema is a common and often frustrating condition, but it is important to remember that it is possible to reduce symptoms and enjoy healthier skin with the proper management strategies. Regular moisturizing, avoiding triggers, managing stress, and following a healthy diet are all essential to managing eczema. If you struggle with eczema, remember that there is hope. Consult a dermatologist to develop a personalized treatment plan that meets your needs.