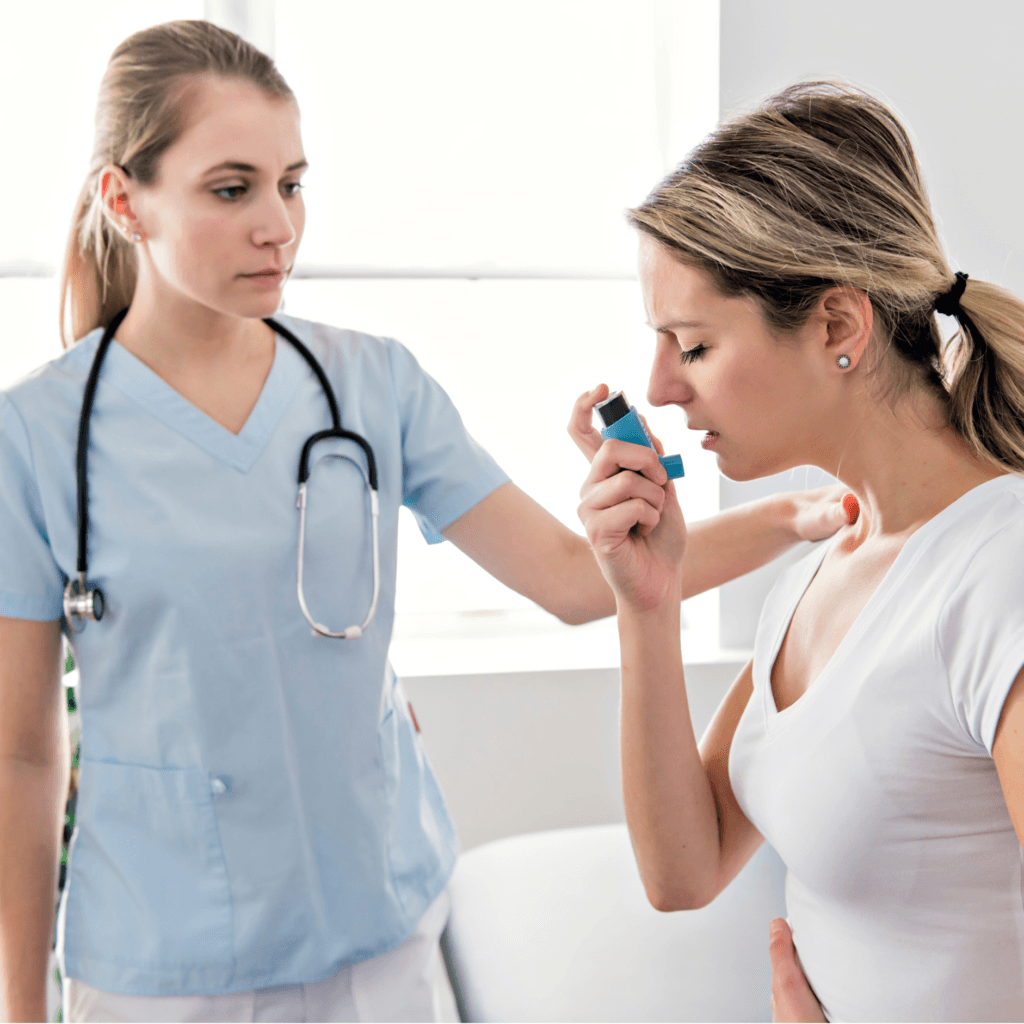Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, asthma can cause episodes of wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. While asthma is a lifelong condition, it is possible to manage and reduce the frequency of asthma episodes through lifestyle modifications. In this blog post, we will explore the prevalence of asthma and discuss how specific lifestyle changes can help manage the condition.
Asthma is not just a personal struggle but a global health issue. It is one of the most common chronic diseases, affecting people of all ages. According to recent statistics, over 262 million people globally have asthma, with nearly 500,000 asthma-related deaths reported annually. In the U.S., approximately 25 million people have asthma, which includes 1 in 13 adults and 1 in 12 children. It is a leading cause of children’s missed school days and workdays among adults. Asthma affects about 8% of Canadians, with a higher prevalence in children, particularly boys. Asthma rates have increased over the past few decades, making it a significant public health concern. Various factors, including allergens, pollution, respiratory infections, physical activity, and stress can trigger asthma. The condition can vary in severity from mild to life-threatening, underscoring the importance of effective management.
HOW CAN LIFESTYLE MODIFICATIONS REDUCE ASTHMA EPISODES?
While asthma cannot be cured, managing the condition is within your control and can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of asthma episodes. Here’s how lifestyle modifications can empower you to take charge of your health and help:
MAINTAIN A HEALTHY WEIGHT
Being overweight or obese can exacerbate asthma symptoms, as excess weight can put pressure on the lungs and airways. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is crucial for asthma management:
Balanced Diet
Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. These foods provide essential nutrients that support overall health and help maintain a healthy weight.
Regular Exercise
Engage in physical activities that promote cardiovascular health without triggering asthma symptoms. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, walking, or cycling are often well-tolerated by people with asthma.
IDENTIFY AND AVOID TRIGGERS
Environmental factors often trigger asthma episodes. By identifying and avoiding these triggers, you can take proactive steps to reduce the occurrence of asthma episodes significantly:
Allergens
Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, pet dander, and mold. Minimize exposure by keeping your home clean, using air purifiers, and avoiding outdoor activities during high pollen counts.
Air Quality
Poor air quality, including pollution and smoke, can trigger asthma symptoms. Monitor local air quality reports and stay indoors when pollution levels are high.
Respiratory Infections
Colds and flu can exacerbate asthma. To reduce risk, practice good hygiene, get vaccinated, and avoid close contact with sick individuals.
STAY ACTIVE WITH SAFE EXERCISE
While exercise can be a trigger for some people with asthma, regular physical activity is essential for maintaining lung function and overall health. To exercise safely:
Warm-Up
Always warm up before exercising to gradually increase your heart rate and reduce the likelihood of an asthma episode.
Choose the Right Activity
Opt for activities that are less likely to trigger symptoms, such as swimming, which can be beneficial due to the moist air in the pool environment.
Monitor Your Symptoms
Pay attention to your body and stop exercising if you experience wheezing, shortness of breath, or chest tightness. Carry your inhaler with you at all times.
HEALTHY DIET AND NUTRITION
Certain foods and dietary habits can influence asthma symptoms. A healthy diet can help reduce inflammation and support lung health:
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Incorporate foods rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids, such as berries, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish. These foods can help reduce inflammation in the airways.
Avoid Trigger Foods
Some people with asthma may be sensitive to certain foods, such as sulfites (found in wine, dried fruits, and processed foods), which can trigger symptoms. Pay attention to your body’s reactions and avoid foods that worsen your asthma.
MANAGE STRESS AND ANXIETY
Stress and anxiety can trigger asthma episodes in some individuals. Learning to manage stress effectively is essential for reducing the occurrence of asthma episodes:
Relaxation Techniques
Deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress and improve lung function.
Adequate Sleep
Ensure you sleep enough each night, as poor sleep can exacerbate asthma symptoms. Establish a regular sleep routine and create a calming environment to promote restful sleep.
QUIT SMOKING AND AVOID SECONDHAND SMOKE
Smoking is a significant risk factor for asthma, as it irritates the airways and can lead to chronic inflammation. Quitting smoking is one of the most effective ways to improve asthma symptoms:
Seek Support
If you smoke, consider joining a smoking cessation program or seeking help from a healthcare provider to quit.
Avoid Secondhand Smoke
Even if you don’t smoke, exposure to secondhand smoke can trigger asthma episodes. Avoid environments where smoking is prevalent.
Asthma is a prevalent and chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. However, with the proper lifestyle modifications, it is possible to manage asthma effectively and reduce the frequency of asthma episodes. Maintaining a healthy weight, identifying and avoiding triggers, staying active with safe exercise, following a nutritious diet, managing stress, and avoiding smoking are all critical steps in managing asthma. By taking control of your lifestyle, you can improve your quality of life and reduce the impact of asthma on your daily activities.